MISO Transmission Expansion Plan (MTEP)
The annual MISO Transmission Expansion Plan (MTEP) is the culmination of a comprehensive, stakeholder-inclusive planning process to build and maintain an electric infrastructure to meet local and regional reliability standards, enable competition among wholesale capacity and energy suppliers in the MISO markets, and allow for competition among transmission developers.
MTEP includes projects from local reliability planning, regional (or long range transmission planning), and interregional planning.
MTEP provides value for customers by ensuring a cost-effective, reliable system that supports policy requirements. Transmission owners submit projects designed to address local reliability issues, aging equipment, load growth and generator interconnection needs, and ensure compliance with NERC standards. Projects are vetted through an 18-month process with more than 75 stakeholder meetings, including a series of public Subregional Planning Meetings (SPM) for each MISO subregion and additional Technical Study Task Force (TSTF) meetings. Since 2003, nearly $60 billion in projects have been approved.
The annual plan is reviewed by the Planning Advisory Committee which recommends approval by MISO’s System Planning Committee of the Board of Directors. The full Board of Directors provides final approval each December.
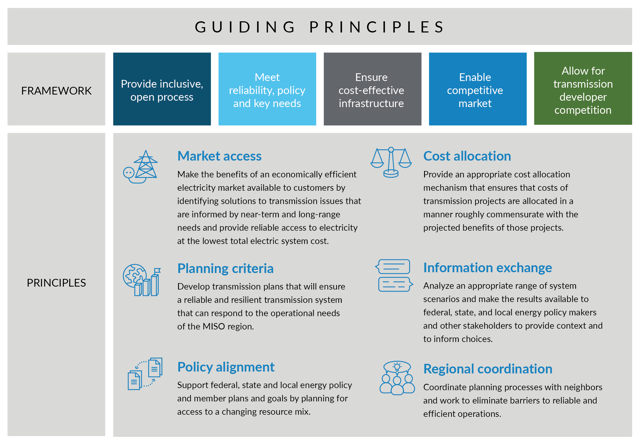
In its planning approach, MISO follows its Tariff, NERC reliability standards, and standards adopted by Regional Reliability Organizations. Guiding Principles that were adopted by MISO’s Board with stakeholder input also provide overarching direction to MISO as it fulfills its planning obligations. Full details about MISO’s comprehensive planning process can be found in its Transmission Planning Business Practices Manual (BPM-020).
MTEP Project Types
After being vetted through the planning process, MTEP Appendix A projects typically fall into one of the following categories:
- Baseline Reliability Projects (BRP), which are required to meet standards for both North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) and local reliability
- Generator Interconnection Projects (GIP) are needed to reliably connect new generation to the transmission grid.
- Market Efficiency Projects (MEP) address congestion within the MISO region or as an interregional project along the seam.
- Market Participant Funded Projects (MPFP) provide network upgrades fully funded by a Market Participant, but owned and operated by an incumbent transmission owner.
- Multi-Value Projects (MVP) top-down projects developed by MISO through Long Range Transmission Planning with stakeholder input to address regional public policy, economic and/or reliability benefits.
- Other Projects address local reliability issues and/or provide local economic benefits but don’t meet the threshold to qualify as Market Efficiency Projects.
- Targeted Market Efficiency Projects (TMEP) are low-cost interregional projects with short lead times to relieve known market-to-market congestion.
- Transmission Deliverability Service Projects (TDSP) are network upgrades required to facilitate long term point-to-point transmission service request.
Planning is underway for MTEP 25. MISO follows an approximate timeline for data requests, postings and email notifications for TPL-001 and planning stakeholder meetings. It roughly follows the 18-month MTEP calendar ending in December each year.
| Month | Item |
| June | Transmission Owners provide any updates to the posted transmission planning criteria and provide any models used to support the identification of proposed projects |
| September | All project submittals due by the 15th |
| January |
First Subregional Planning Meeting (SPM) MISO requests steady state contingencies from Transmission Owners |
| February |
FERC 715 data filing request form sent |
| May |
MISO posts steady state results for single initiating events for Transmission Owner review Deadline to submit project alternatives by the 31st Second Subregional Planning Meeting (SPM) |
| June |
Second Subregional Planning Meeting (SPM) MISO posts steady state results for P3-P6 events for Transmission Owner review |
| August |
TPL-001, MISO posts transient results for Transmission Owner Review Third Subregional Planning Meeting (SPM) |
| November | TPL-001, MISO posts extreme events steady state results for Transmission Owner review |
| December | MISO posts MTEP confidential appendices |
The 2024 MISO Transmission Expansion Plan (MTEP24) marks a pivotal milestone in solidifying the region’s future reliability. The plan’s 488 projects address critical needs across the footprint and deliver significant value to MISO’s customers. Together with the existing grid, these new projects seek to ensure the lights stay on for 45 million people today and for years to come.
- Local reliability: Traditional MTEP projects strengthen local transmission to meet the growing demand for electricity in an increasingly dynamic environment.
- Regional (LRTP Tranche 2.1): The highly anticipated LRTP Tranche 2.1 Portfolio establishes a ground-breaking transmission backbone and delivers benefits that exceed costs.
- Joint Targeted Interconnection Queue (JTIQ): The SPP-MISO JTIQ Portfolio unlocks the potential for approximately 28 GW of generation interconnections, eliminating barriers to new capacity at the SPP-MISO seam.
- MTEP24 Executive Summary
- MTEP24 Full Report
- MTEP24 Chapter 1 – Transmission Planning Overview
- MTEP24 Chapter 2 – Regional Long Range Transmission Planning
- MTEP24 Chapter 3 – Interregional Planning
- MTEP24 Chapter 4 – Local Reliability Planning
- MTEP24 Appendix F – Stakeholder Substantive Comments
- MTEP24 Appendix A – LRTP Tranche 2.1 Projects
- MTEP24 Appendix A – JTIQ Projects
- MTEP24 Appendix A – New Local Reliability Projects
- MTEP24 A-1, A-2 New Projects Cost Allocations
- MTEP24 A-3 Active Projects – Previously approved projects not yet in service
- LRTP Tranche 2.1 Appendix A-4 Schedule 26A Indicative
Projects submitted for MTEP are vetted through an 18-month process that begins in June of the year prior to approval. New MTEP projects must be submitted by September 15th each year for the next MTEP study cycle. Alternatives to these MTEP projects must be submitted by the latter of May 31st or by the Second Subregional Planning Meeting (SPM2). For more information on schedules and requirements, see MTEP Information Exchange Schedules and Requirements.
MTEP Portal
Throughout the application process, and after approval during a project’s lifecycle, project information is captured and reported through MISO’s MTEP Portal. The MTEP Portal can be accessed in the MISO Help Center. For detailed instructions on how to access and use the tool, see the MTEP Portal User Guide.
Transmission Owners can reach out to their MISO Expansion Planner representative to receive additional support as needed.
Market Participant Funded Projects
Non transmission owners who need to submit Market Participant Funded Projects for MTEP will need to do so using the Market Participant Funded Project Request Form.
Expedited Project Review Request
Some circumstances require projects to be approved prior to the next annual MTEP cycle. Transmission owners may justify an Expedited Project Review (EPR) study if it will help drive a timely response to a significant load additions or other new system needs that require budgeting, regulatory milestones, construction and other project development support prior to approval of the next MTEP.
On the first business day of every even month, beginning June 2025, MISO will close the submittal window and begin an EPR study cycle to analyze all completed EPR requests received prior to the beginning of the study. Any EPRs submitted after the closing of the submittal window will be studied in the next EPR study cycle. MISO will provide notification of all EPRs to be studied each cycle. On the first Tuesday each month, MISO will host a Technical Studies Task Force (TSTF) meeting to present EPRs which have completed technical analysis and mitigation requirements as specified under NERC Standard TPL-001. Please refer to BPM-020 section 4.1.4 for a complete description of the updated process.
Submit requests using the Expedited Project Review Request Form.
Project Alternative Submission
The MTEP process will consider proposed alternative solutions to Transmission Owners submitted projects. Entities interested in proposing alternatives are required to complete and submit the MTEP Project Alternative Submittal Form.
Contact the Expansion Planning Team with any questions or issues.
MTEP project information is updated quarterly by transmission owners and monitored by MISO utilizing the MTEP Portal, which provides historical and the most current reports and data. The MTEP application process is also managed through the MTEP Portal.
Project Lists and Status Reports
Several status reports on approved MTEP Appendix A projects and projects under evaluation are always available in the MTEP Portal. Quarterly project updates are available in the Documents section found at the bottom of this web page. Other reports include the following:
- MTEP Projects Under Evaluation: Projects under review in the current MTEP cycle.
- MTEP Appendix A Status Report: Approved Appendix A projects and facilities from the previous MTEP cycle with quarterly updates to the construction status, estimated in-service and estimated cost until a facility goes into service.
- MTEP Status Report Dashboard: Project statistics from the Appendix A status report.
- MTEP In-Service Projects: In-service projects from all MTEP cycles.
- MVP Dashboard: Status dashboard for all MVP projects.
Variance Analysis
MISO monitors project approved in MTEP Appendix A to determine if certain circumstances or events may significantly affect the cost, schedule and or the ability of selected developers and transmission owners to continue the designated eligible project.
If potential issues are discovered, MISO may perform a three-phase variance analysis to further understand the reasons for such circumstances or events and to evaluate any potential impacts that they may have on the successful completion of the project or on the transmission system. Learn more about this process in the MISO Tariff, Attachment FF, Section IX.
Schedule 26 and 26A Indicative Reports
MISO produces indicative forecasts of Schedule 26 and 26-A annual charges (by MISO Pricing Zone) for cost-shared projects approved by MTEP. Indicative Schedule 26 annual charges are based on approved Baseline Reliability Projects, Generation Interconnection Projects, Market Efficiency Projects, and Targeted Market Efficiency Projects. Indicative Schedule 26-A annual charges are based on approved Multi-Value Projects.
These reports are typically updated annually in the second quarter. Values are intended to be indicative only, should not be relied upon for settlement or ratemaking purposes, and are subject to change.
Planning Advisory Committee (PAC)
System Planning Committee (SPC)
Subregional Planning Meetings (SPM)
Regional Expansion Criteria and Benefits Working Group (RECBWG)
Interconnection Process Working Group (IPWG)
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How do I access reliability models? Models are posted on the MISO FTP. To request FTP access, please fill out the access request form and request "FTP Sites."
2. How do I access MTEP transmission maps? There are two ways to access the MTEP transmission maps. The first is to fill out the access request form and request "Maps."
3. How do I access the MTEP Portal? Instructions to access the MTEP Portal are available in the Help Center.
Please note: To fill out the access request form, a MISO website login is required. To receive FTP access, appropriate CEII NDAs and UNDAs must be on file. Additional information about NDA forms can be found on the Client Services and Readiness page.
Contact the Expansion Planning Team with any questions or issues.